Food Price Inflation: US Outlook 4% Increase by June 2025

Current projections indicate a 4% rise in US food prices by June 2025, underscoring ongoing inflationary pressures across the nation’s food supply chain.
Recent economic forecasts are signaling a significant challenge for American households, as Inflationary Pressures: A 6-Month Outlook on Food Prices in the US, Expecting a 4% Increase by June 2025 is now firmly on the horizon. Consumers can anticipate a continued squeeze on their budgets, with experts projecting a notable uptick in grocery costs.
Understanding the Current Inflationary Landscape
The United States economy continues to grapple with persistent inflationary forces, particularly impacting the food sector. Various factors, from supply chain disruptions to geopolitical events, are contributing to this complex environment, making it challenging for both producers and consumers.
As of late 2024, the underlying drivers of food price increases remain robust. Analysts are closely monitoring key economic indicators to predict future movements, with recent data suggesting a sustained upward trajectory.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Ongoing issues in global logistics and transportation networks are significant contributors to rising food costs. Delays at ports, labor shortages, and increased shipping expenses directly translate to higher prices on supermarket shelves.
- Port congestion and container shortages
- Increased fuel costs for transportation
- Labor availability challenges across the supply chain
Impact of Geopolitical Events
International conflicts and trade disputes often have a ripple effect on global commodity markets, including essential foodstuffs. These events can disrupt production, limit exports, and create uncertainty, pushing prices higher.
Key Factors Driving the 4% Increase by June 2025
The anticipated 4% increase in US food prices by June 2025 is not a singular event but the culmination of several interconnected economic and environmental factors. Understanding these drivers is crucial for both policymakers and consumers to prepare for the coming months.
Agricultural commodity prices, energy costs, and labor expenses are among the primary components contributing to this projected rise. Each element plays a substantial role in the final cost consumers pay for their groceries.
Rising Agricultural Commodity Prices
The cost of raw agricultural products, such as grains, livestock, and produce, forms the foundation of food prices. Adverse weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and shifts in global demand can significantly impact these prices.
- Droughts and floods affecting crop yields
- Increased demand from emerging markets
- Higher input costs for fertilizers and seeds
Energy Costs and Transportation
Energy is a critical component in every stage of food production and distribution, from farming machinery to processing plants and transportation. Fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices directly influence the cost of bringing food to market.
Fuel expenses for trucks, ships, and planes that transport food across vast distances are a major overhead for distributors. Any upward movement in global energy markets inevitably translates into higher expenses for consumers.
Consumer Spending Habits and Household Budgets
The projected 4% increase in food prices will inevitably place additional strain on household budgets across the US. Consumers are already feeling the pinch from previous inflationary periods, and this new forecast suggests a continued need for adaptation and strategic spending.
Many families will likely need to re-evaluate their grocery lists, seek out more affordable alternatives, and potentially reduce discretionary spending to accommodate higher essential costs. This shift in purchasing behavior could have broader implications for the retail food industry.
Strategies for Managing Higher Costs
Households are increasingly employing various strategies to mitigate the impact of rising food prices. These include more careful meal planning, bulk purchasing, and seeking out sales and discounts.
- Increased meal preparation at home
- Shopping at discount retailers or farmers’ markets
- Reducing food waste through better planning
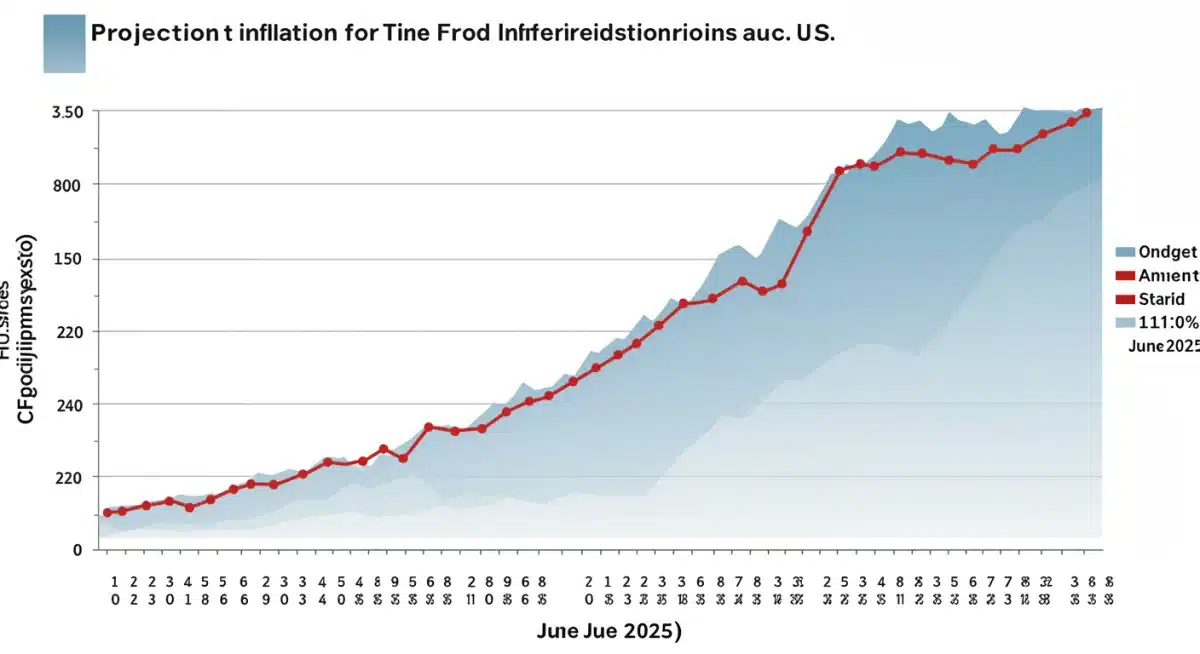
Government and Industry Responses to Food Inflation
Both government bodies and the food industry are actively seeking ways to address and mitigate the impact of rising food prices. These efforts range from policy interventions to innovative business strategies aimed at stabilizing costs and supporting consumers.
Regulatory measures, subsidies, and initiatives to improve supply chain efficiency are all being explored as potential solutions. The goal is to balance the needs of producers with the affordability concerns of consumers.
Policy Interventions and Support Programs
Government agencies are considering various policy tools to alleviate inflationary pressures. These may include targeted subsidies for agricultural producers, adjustments to trade policies, or direct assistance programs for low-income families.
Discussions are ongoing regarding the effectiveness and feasibility of different interventions, with a focus on long-term sustainability rather than temporary fixes. The aim is to create a more resilient food system.
Regional Variations in Food Price Increases
While the national average projects a 4% increase, it is crucial to recognize that the impact of food price inflation will not be uniform across all regions of the United States. Local market dynamics, transportation costs, and regional supply chain efficiencies can lead to significant variations.
Urban centers with higher distribution costs might experience more pronounced increases, while agricultural regions could see different trends. Consumers should be aware of these localized differences when assessing their personal financial outlook.
Factors Influencing Regional Disparities
Several elements contribute to how food prices fluctuate from one state or city to another. These include proximity to production centers, local taxes, and the competitive landscape of regional grocery markets.
- Transportation distance from farms to markets
- Local and state tax structures on food items
- Concentration of grocery retailers in specific areas
Long-Term Economic Outlook and Future Projections
Beyond the immediate six-month forecast, economists are also examining the long-term trajectory of food prices and their implications for the broader US economy. The current inflationary period may represent a shift in fundamental economic conditions rather than a temporary anomaly.
Factors such as climate change, population growth, and evolving global trade relationships are expected to continue influencing food security and pricing for years to come. Strategic planning for future resilience is becoming increasingly vital.
Investment in agricultural technology, sustainable farming practices, and diversified supply chains are seen as essential steps to build a more stable food system. These long-term initiatives aim to mitigate future price shocks and ensure continued access to affordable food.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Projected Increase | US food prices are expected to rise by 4% by June 2025. |
| Key Drivers | Supply chain issues, energy costs, and agricultural commodity prices are major contributors. |
| Consumer Impact | Households will face increased budget strains, necessitating adaptive spending strategies. |
| Regional Variations | Price increases will vary by region due to local market conditions and distribution. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Food Price Inflation
The anticipated 4% rise in US food prices by June 2025 stems from a combination of global supply chain disruptions, elevated energy costs, and fluctuating agricultural commodity prices due to environmental and geopolitical factors.
American households can expect increased strains on their budgets. They may need to adjust spending habits, seek cheaper alternatives, and plan meals more carefully to manage the higher costs of essential food items effectively.
While broad increases are expected, categories heavily reliant on specific commodities like grains, meat, and fresh produce are particularly vulnerable. Energy-intensive processing and transportation also affect packaged goods significantly.
Governments and industry are exploring policy interventions such as subsidies, trade adjustments, and investments in supply chain efficiency. These efforts aim to stabilize prices and support consumers through both short-term and long-term strategies.
Long-term projections suggest that factors like climate change, population growth, and evolving global trade dynamics will continue to influence food prices. Investments in sustainable agriculture are crucial for future price stability beyond the immediate forecast.
Looking Ahead
The projected 4% increase in US food prices by June 2025 signifies a critical period for both consumers and economic stability. This development underscores the ongoing volatility within global markets and the persistent challenges facing the food supply chain. As these inflationary pressures continue, monitoring government responses, industry innovations, and consumer adaptation strategies will be essential. The coming months will provide crucial insights into the resilience of the economy and the effectiveness of measures implemented to mitigate the impact on everyday Americans.